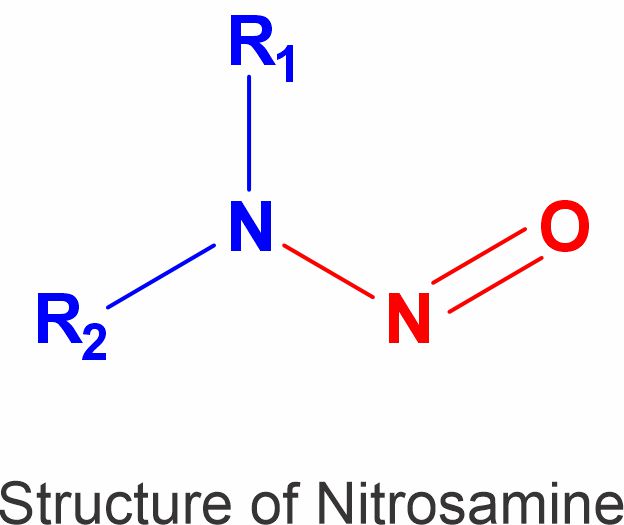
What are nitrosamines ?
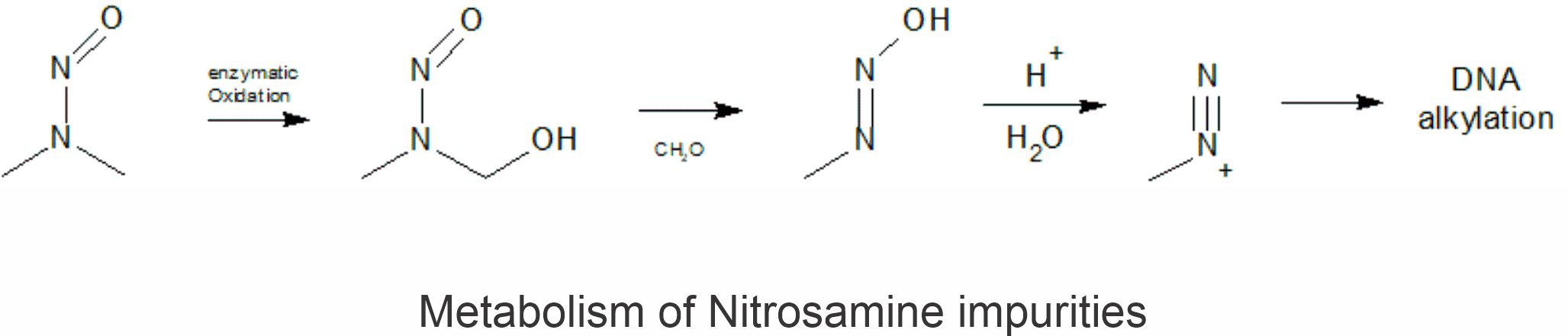
N-nitroso compounds, also called Nitrosamines, are a class of indirect-acting mutagens, as their metabolic degradation leads to the formation of the DNA-alkylating diazonium ion.
Hence, the toxicity of these Nitrosamines has been studied for many years, starting with N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA), which, with early evidence in 1956, was found to induce tumors in the liver of rats, providing an early indication of its potential health risks.
The carcinogenicity of Nitrosamine compounds was extensively studied by Jerzy Lijinsky, published in 1987, which discusses various aspects of Nitrosamine compounds, including their presence in the diet and their potential role as carcinogens. The target site and potency vary with species, age, dose, and route of exposure. Common target organs for N-nitrosamines in rats are the liver, esophagus, respiratory tract, kidneys, and bladder.
Concerns about nitrosamine contamination in drugs became prominent in recent years when some medications were found to contain unacceptable levels of nitrosamines. The presence of nitrosamines in drugs has led to recalls and regulatory actions to ensure the safety of pharmaceutical products. Regulatory agencies, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), have set limits for acceptable levels of nitrosamines in pharmaceuticals.
Nitrosamines can form through the reaction of secondary, tertiary or quaternary amines with nitrosating agents. The nitrosation process involves the conversion of amines (compounds containing nitrogen and hydrogen) into nitroso compounds. The nitrosation reaction is typically favored in acidic or mildly acidic environments.
DNA alkylation by nitrosamine compounds involves metabolic oxidative activation, followed by decomposition to yield alkylating species which react DNA base present in genes & thus bring mutation in gene which may lead to cancer. Nitrosamines lacking any α-carbon hydrogens or heteroatom are indicated to be of lower concern.
Nitrosamine impurities can get incorporated into the drug substance and drug product basically through process formation, direct introduction, degradation or cross-contamination. Manufacturing of drug substances involves raw material, intermediates, solvents, chemicals and reagents [7-9]. Through these stages, if this impurity is formed or present it may get incorporated and carried forwarded to drug product.
Nitrosamine Drug Substance Related Impurities (NDSRIs)
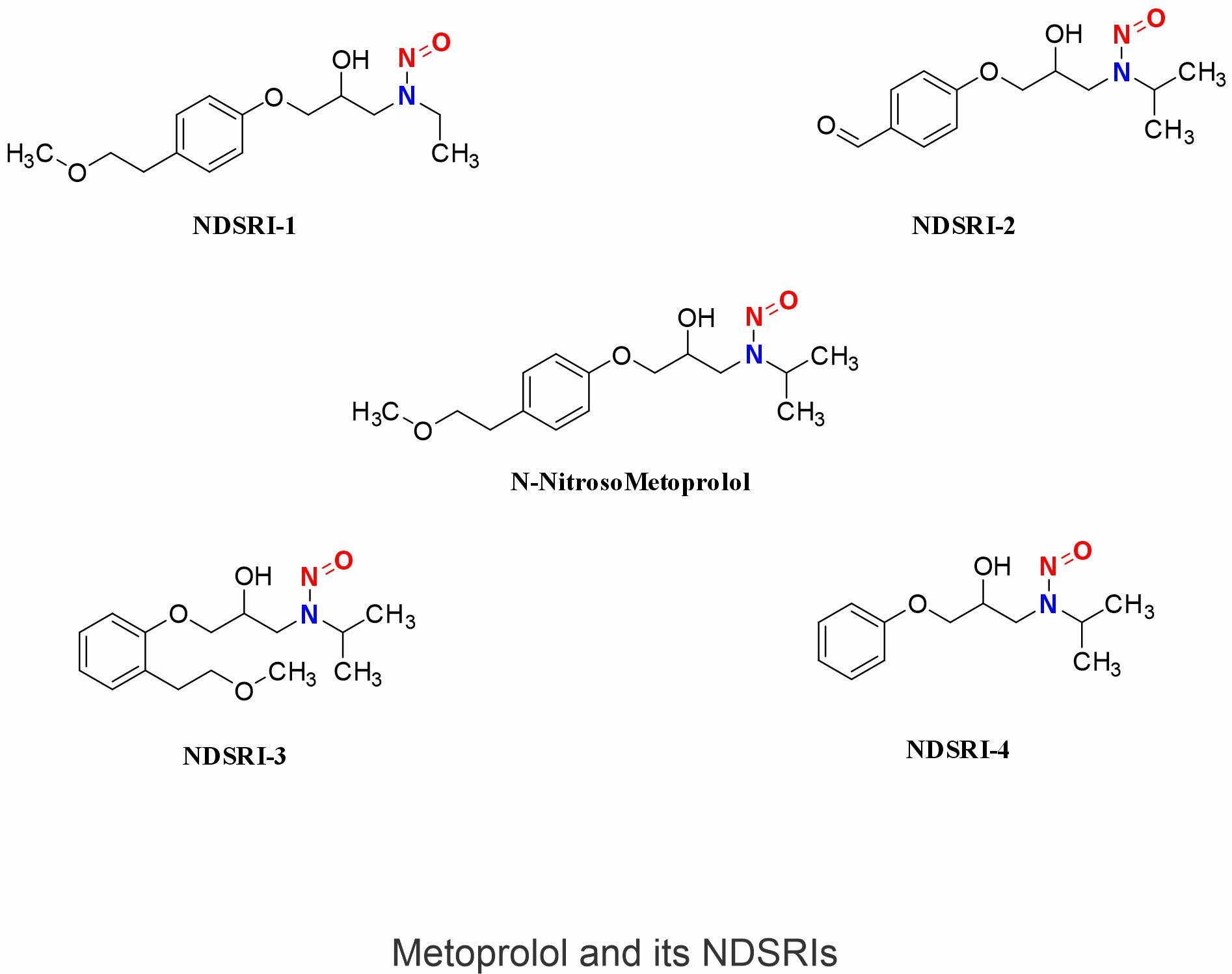
These are a class of nitrosamine impurities that have been identified in many drug substances and drug products. NDSRIs have a structure similar to that of drug substances or their impurities with a nitrosamine as a functional group. EMA defines NDSRI are ‘Active substance-derived nitrosamines impurities’. Based on their structure, it can be said that all NDSRI are nitrosamine but all nitrosamine are not NDSRI. Metoprolol and its impurity molecules have secondary amines in their functional groups in their structure, where all of these molecules can form the NDSRIs. in the presence of a trace amount of nitrosating agent.
Keywords: Impurities, Nitrosamine, Classification, Guidelines, Drug substances, Drug product, NDSRI